Critical Care
Fresenius Kabi manufactures a diverse collection of drugs essential to the management of critically and chronically ill patients, including, but not limited to, anticoagulants, cardiovascular agents, antiemetics, anti-inflammatory agents, and CNS drugs.
Featured Products
Glucagon for Injection
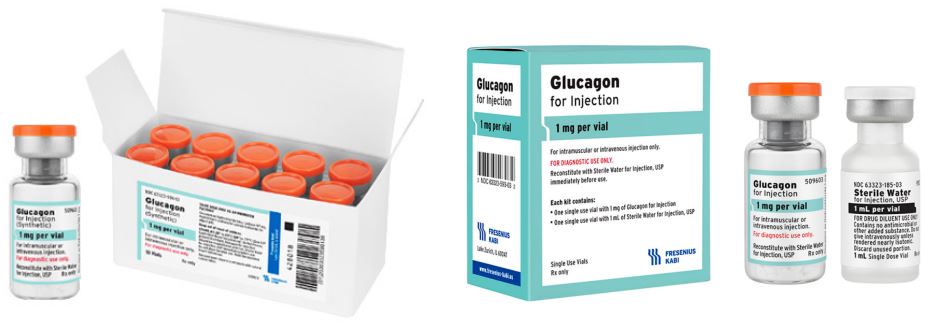
Discover the only Glucagon for Injection vial designed for diagnostic use in the U.S.*
Available in convenient single-dose vials or kits, it’s an option for use during radiologic
examinations to temporarily inhibit movement of the gastrointestinal tract in adult
patients. For more information click here.
Available in:
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Pheochromocytoma
- Insulinoma
- Known hypersensitivity to glucagon or to any of the excipients.
- Glucagonoma when used as a diagnostic aid
WARNINGS AND PRECATUIONS
- Catecholamine Release in Patients with Pheochromocytoma: Contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because Glucagon for Injection may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor.
- Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma: In patients with insulinoma, administration may produce an initial increase in blood glucose; however, Glucagon for Injection may stimulate exaggerated insulin release from an insulinoma and cause hypoglycemia. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of Glucagon for Injection, give glucose orally or intravenously.
- Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions have been reported and include generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension.
- Lack of Efficacy in Patients with Decreased Hepatic Glycogen: Glucagon for Injection is effective in treating hypoglycemia only if sufficient hepatic glycogen is present. Patients in states of starvation, with adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia may not have adequate levels of hepatic glycogen for Glucagon for Injection to be effective. Patients with these conditions should be treated with glucose.
- Necrolytic Migratory Erythema (NME): a skin rash, has been reported postmarketing following continuous glucagon infusion and resolved with discontinuation of the glucagon. Should NME occur, consider whether the benefits of continuous glucagon infusion outweigh the risks.
- Hyperglycemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus when Used as a Diagnostic Aid: Treatment with Glucagon for Injection in patients with diabetes mellitus may cause hyperglycemia. Monitor diabetic patients for changes in blood glucose levels during treatment and treat if indicated.
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increase in Patients with Cardiac Disease when Used as a Diagnostic Aid: Glucagon for Injection may increase myocardial oxygen demand, blood pressure, and pulse rate. Cardiac monitoring is recommended in patients with cardiac disease during use of Glucagon for Injection as a diagnostic aid, and an increase in blood pressure and pulse rate may require therapy.
- Hypoglycemia in Patients with Glucagonoma when Used as a Diagnostic Aid: Glucagon administered to patients with glucagonoma may cause secondary hypoglycemia. Test patients suspected of having glucagonoma for blood levels of glucagon prior to treatment, and monitor blood glucose levels during treatment. If a patient develops hypoglycemia, give glucose orally or intravenously.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (>5% or greater incidence): Injection site swelling, injection site erythema, vomiting, nausea, decreased blood pressure, asthenia, headache, dizziness, pallor, diarrhea, and somnolence.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC, at 1-800-551-7176 option 5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
- Beta-blockers: Patients taking beta-blockers may have a transient increase in pulse and blood pressure.
- Indomethacin: In patients taking indomethacin Glucagon for Injection may lose its ability to raise glucose or may produce hypoglycemia.
- Anticholinergic drugs: Concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs with Glucagon for Injection for use as a diagnostic aid is not recommended.
- Warfarin: Glucagon for Injection may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
- Insulin: Monitor blood glucose when Glucagon for Injection is used as a diagnostic aid in patients receiving insulin.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Glucagon for Injection is a gastrointestinal motility inhibitor indicated for use as a diagnostic aid during radiologic
examinations to temporarily inhibit movement of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in adult patients.
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use Glucagon for Injection
safely and effectively. Please see accompanying full prescribing information for Glucagon for Injection. Full
prescribing information is also available at www.fresenius-kabi.com/us.
Please see Full Prescribing Information
*Per IQVIA as of Feb 2024
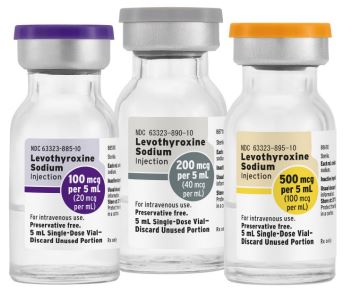
Levothyroxine Sodium Injection
Ready-to-use for optimal care
- Helps promote sate medication practices
- May improve operational efficiency
- Reduces waste
Available strengths:
Experience the convenience of ready-to-use vials with Levothyroxine Sodium Injection
from Fresenius Kabi. Available in various strengths, these vials may help improve
efficiency and reduce waste. For more information click here.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION

Levothyroxine Sodium Injection is contraindicated in uncorrected adrenal insufficiency.
Cardiac Adverse Reactions in the Elderly and in Patients with Underlying Cardiovascular Disease: Overtreatment may cause arrhythmias, tachycardia, myocardial ischemia and infarction, or worsening of congestive heart failure and death, particularly in patients with cardiovascular disease and in elderly patients. Start with lower doses in elderly patients and in patients with underlying cardiovascular disease and monitor patients after administration.
Acute Adrenal Crisis in Patients with Concomitant Adrenal Insufficiency: Initiation of thyroid hormone therapy prior to initiating glucocorticoid therapy may precipitate an acute adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency. Treat patients with adrenal insufficiency with replacement glucocorticoids prior to initiating treatment.
Worsening of Diabetic Control: May worsen glycemic control and result in increased antidiabetic agent or insulin requirements. Carefully monitor glycemic control.
Adverse reactions associated with Levothyroxine Sodium Injection are primarily those of hyperthyroidism due to therapeutic overdosage: fatigue, increased appetite, weight loss, heat intolerance, fever, excessive sweating, headache, hyperactivity, nervousness, anxiety, irritability, emotional lability, insomnia, tremors, muscle weakness, muscle spasm, palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmias, increased pulse and blood pressure, heart failure, angina, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, dyspnea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, elevations in liver function tests, flushing, and rash.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176, option 5, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See Full Prescribing Information for drugs that affect thyroid hormone pharmacokinetics and metabolism (e.g., synthesis, secretion, catabolism, protein binding, and target tissue response) that may alter the therapeutic response to Levothyroxine Sodium Injection.
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use
Levothyroxine Sodium Injection safely and effectively. Please see accompanying full prescribing
information for Levothyroxine Sodium Injection. Full prescribing information is also available at
www.fresenius-kabi.com/us.
To place an order, contact your Sales Representative or call Customer Service
at 1.888.386.1300 | www.fresenius-kabi.com/us
